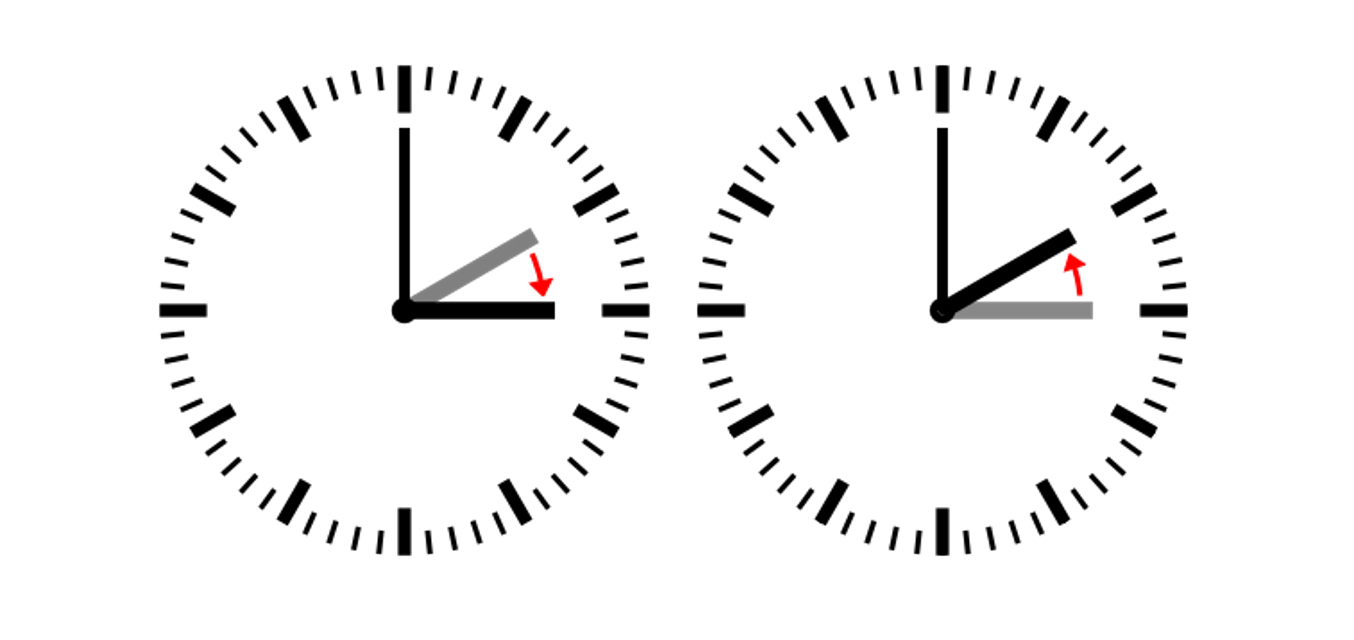
Did you know that Daylight Saving Time was first introduced by the German government during World War I?
Germany introduced Daylight Saving Time in 1916, during World War I, primarily to reduce the use of coal, which was urgently needed for the war effort. A large number of European countries adopted Daylight Saving Time shortly thereafter. Daylight Saving Time is a period of about 7 months from the end of March to the end of October, during which many countries adjust their time one hour ahead of standard time. For example, it is 8:00 pm instead of 7:00 pm. Standard time is also known as Winter Time and is considered the “real” time.
The implementation of Daylight Saving Time was done to save energy. The reasoning was that in summer, the sun rises at around 5:00 am when most people are still asleep, and thus the natural light is not being used. By moving the clock forward an hour, this hour of daylight is utilized. Since most people are accustomed to staying up late and tend to go to sleep when it gets dark, there are benefits to be gained in the evening. The sun sets an hour later, which means that artificial lighting is needed an hour later, thereby saving energy.
There is also a lot of criticism of Daylight Saving Time. Many animals that follow human routines have a hard time adjusting to it, such as pets that are fed or walked an hour earlier than usual. Additionally, there are doubts about the argument of energy savings. If it stays light for an extra hour in the evening, people may drive more, which consumes more energy. In various countries, there are proposals to adopt Daylight Saving Time as the standard time, eliminating the use of Winter Time altogether. This has already been done in countries like Iceland, Russia, and Belarus.